Kafka routine load StarRocks using shared-data storage
About Routine Load
Routine load is a method using Apache Kafka, or in this lab, Redpanda, to continuously stream data into StarRocks. The data is streamed into a Kafka topic, and a Routine Load job consumes the data into StarRocks. More details on Routine Load are provided at the end of the lab.
About shared-data
In systems that separate storage from compute, data is stored in low-cost reliable remote storage systems such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage, and other S3-compatible storage like MinIO. Hot data is cached locally and when the cache is hit, the query performance is comparable to that of storage-compute coupled architecture. Compute nodes (CN) can be added or removed on demand within seconds. This architecture reduces storage costs, ensures better resource isolation, and provides elasticity and scalability.
This tutorial covers:
- Running StarRocks, Redpanda, and MinIO with Docker Compose
- Using MinIO as the StarRocks storage layer
- Configuring StarRocks for shared-data
- Adding a Routine Load job to consume data from Redpanda
The data used is synthetic.
There is a lot of information in this document, and it is presented with step-by-step content at the beginning, and the technical details at the end. This is done to serve these purposes in this order:
- Configure Routine Load.
- Allow the reader to load data in a shared-data deployment and analyze that data.
- Provide the configuration details for shared-data deployments.
Prerequisites
Docker
- Docker
- 4 GB RAM assigned to Docker
- 10 GB free disk space assigned to Docker
SQL client
You can use the SQL client provided in the Docker environment, or use one on your system. Many MySQL-compatible clients will work, and this guide covers the configuration of DBeaver and MySQL Workbench.
curl
curl is used to download the Compose file and the script to generate the data. Check to see if you have it installed by running curl or curl.exe at your OS prompt. If curl is not installed, get curl here.
Python
Python 3 and the Python client for Apache Kafka, kafka-python, are required.
Terminology
FE
Frontend nodes are responsible for metadata management, client connection management, query planning, and query scheduling. Each FE stores and maintains a complete copy of metadata in its memory, which guarantees indiscriminate services among the FEs.
CN
Compute Nodes are responsible for executing query plans in shared-data deployments.
BE
Backend nodes are responsible for both data storage and executing query plans in shared-nothing deployments.
This guide does not use BEs, this information is included here so that you understand the difference between BEs and CNs.
Launch StarRocks
To run StarRocks with shared-data using Object Storage you need:
- A frontend engine (FE)
- A compute node (CN)
- Object Storage
This guide uses MinIO, which is S3 compatible Object Storage provider. MinIO is provided under the GNU Affero General Public License.
Download the lab files
docker-compose.yml
mkdir routineload
cd routineload
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/StarRocks/demo/master/documentation-samples/routine-load-shared-data/docker-compose.yml
gen.py
gen.py is a script that uses the Python client for Apache Kafka to publish (produce) data to a Kafka topic. The script has been written with the address and port of the Redpanda container.
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/StarRocks/demo/master/documentation-samples/routine-load-shared-data/gen.py
Start StarRocks, MinIO, and Redpanda
docker compose up --detach --wait --wait-timeout 120
Check the progress of the services. It should take 30 seconds or more for the containers to become healthy. The routineload-minio_mc-1 container will not show a health indicator, and it will exit once it is done configuring MinIO with the access key that StarRocks will use. Wait for routineload-minio_mc-1 to exit with a 0 code and the rest of the services to be Healthy.
Run docker compose ps until the services are healthy:
docker compose ps
WARN[0000] /Users/droscign/routineload/docker-compose.yml: `version` is obsolete
[+] Running 6/7
�✔ Network routineload_default Crea... 0.0s
✔ Container minio Healthy 5.6s
✔ Container redpanda Healthy 3.6s
✔ Container redpanda-console Healt... 1.1s
⠧ Container routineload-minio_mc-1 Waiting 23.1s
✔ Container starrocks-fe Healthy 11.1s
✔ Container starrocks-cn Healthy 23.0s
container routineload-minio_mc-1 exited (0)
Examine MinIO credentials
In order to use MinIO for Object Storage with StarRocks, StarRocks needs a MinIO access key. The access key was generated during the startup of the Docker services. To help you better understand the way that StarRocks connects to MinIO you should verify that the key exists.
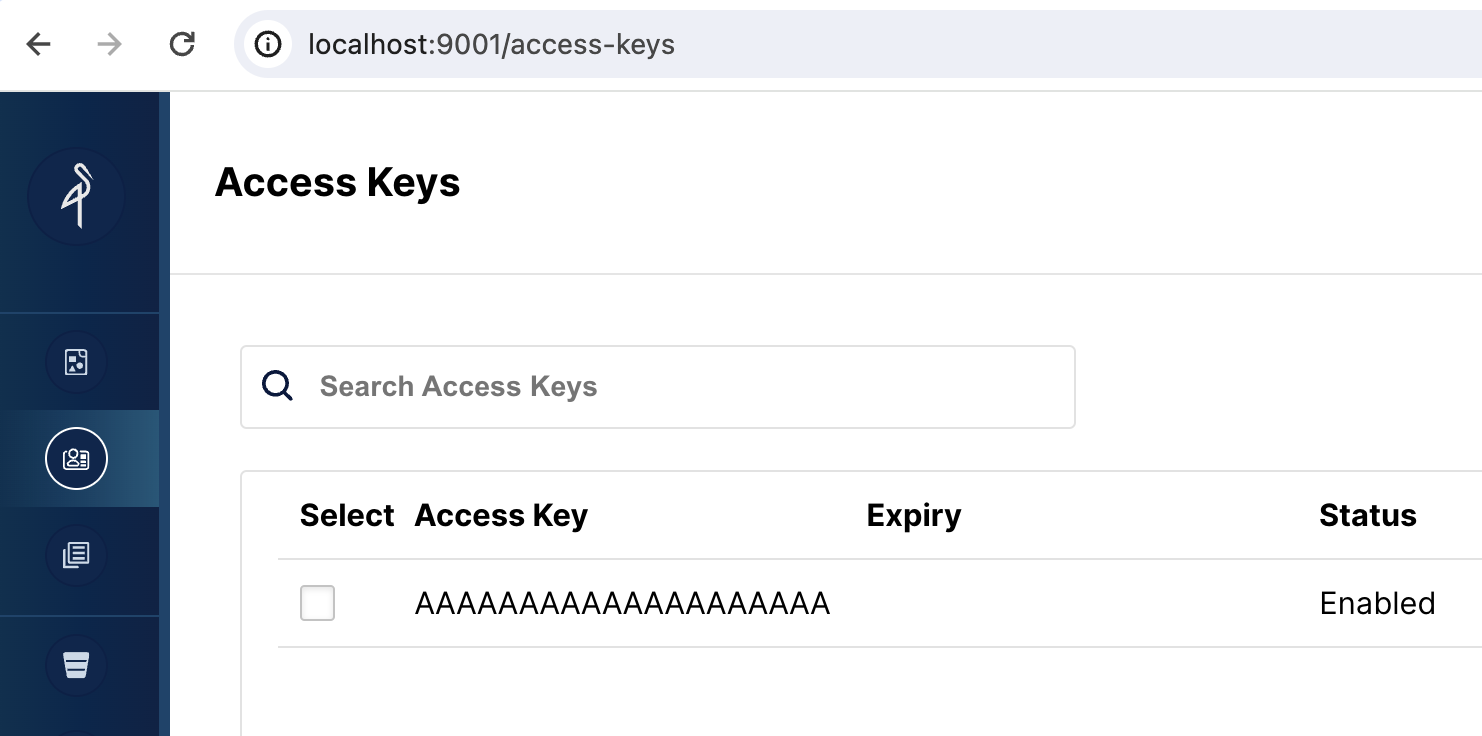
Open the MinIO web UI
Browse to http://localhost:9001/access-keys The username and password are specified in the Docker compose file, and are miniouser and miniopassword. You should see that there is one access key. The Key is AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA, you cannot see the secret in the MinIO Console, but it is in the Docker compose file and is BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB:
Create a bucket for your data
When you create a storage volume in StarRocks you will specify the LOCATION for the data:
LOCATIONS = ("s3://my-starrocks-bucket/")
Open http://localhost:9001/buckets and add a bucket for the storage volume. Name the bucket my-starrocks-bucket. Accept the defaults for the three listed options.
SQL Clients
These three clients are tested with this tutorial, you only need one:
- mysql CLI: You can run this from the Docker environment or your machine.
- DBeaver is available as a community version and a Pro version.
- MySQL Workbench
Configuring the client
- mysql CLI
- DBeaver
- MySQL Workbench
The easiest way to use the mysql CLI is to run it from the StarRocks container starrocks-fe:
docker compose exec starrocks-fe \
mysql -P 9030 -h 127.0.0.1 -u root --prompt="StarRocks > "
All docker compose commands must be run from the directory containing the docker-compose.yml file.
If you would like to install the mysql CLI expand mysql client install below:
mysql client install
- macOS: If you use Homebrew and do not need MySQL Server run
brew install mysql-client@8.0to install the CLI. - Linux: Check your repository system for the
mysqlclient. For example,yum install mariadb. - Microsoft Windows: Install the MySQL Community Server and run the provided client, or run
mysqlfrom WSL.
- Install DBeaver, and add a connection:
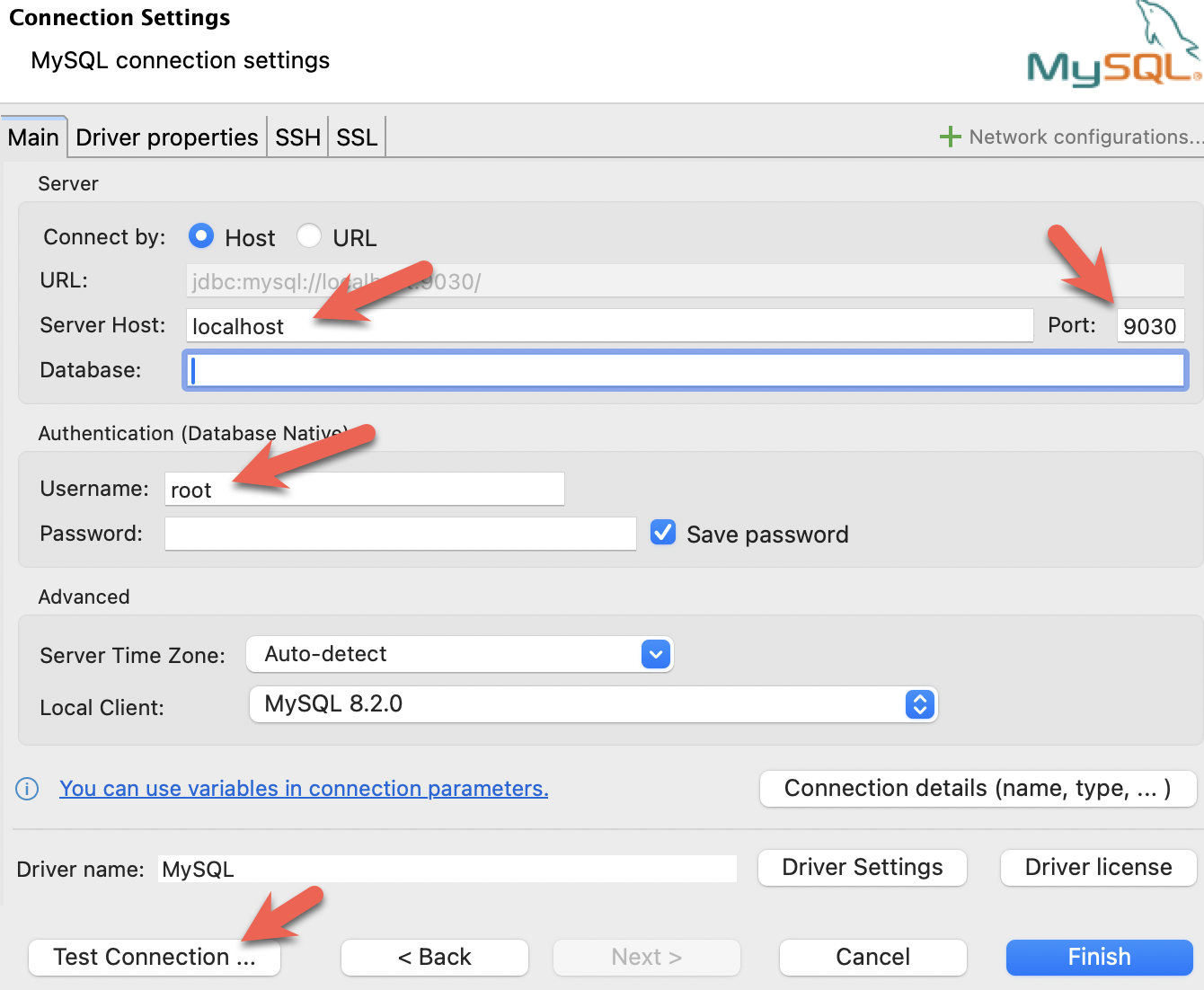
- Configure the port, IP, and username. Test the connection, and click Finish if the test succeeds:
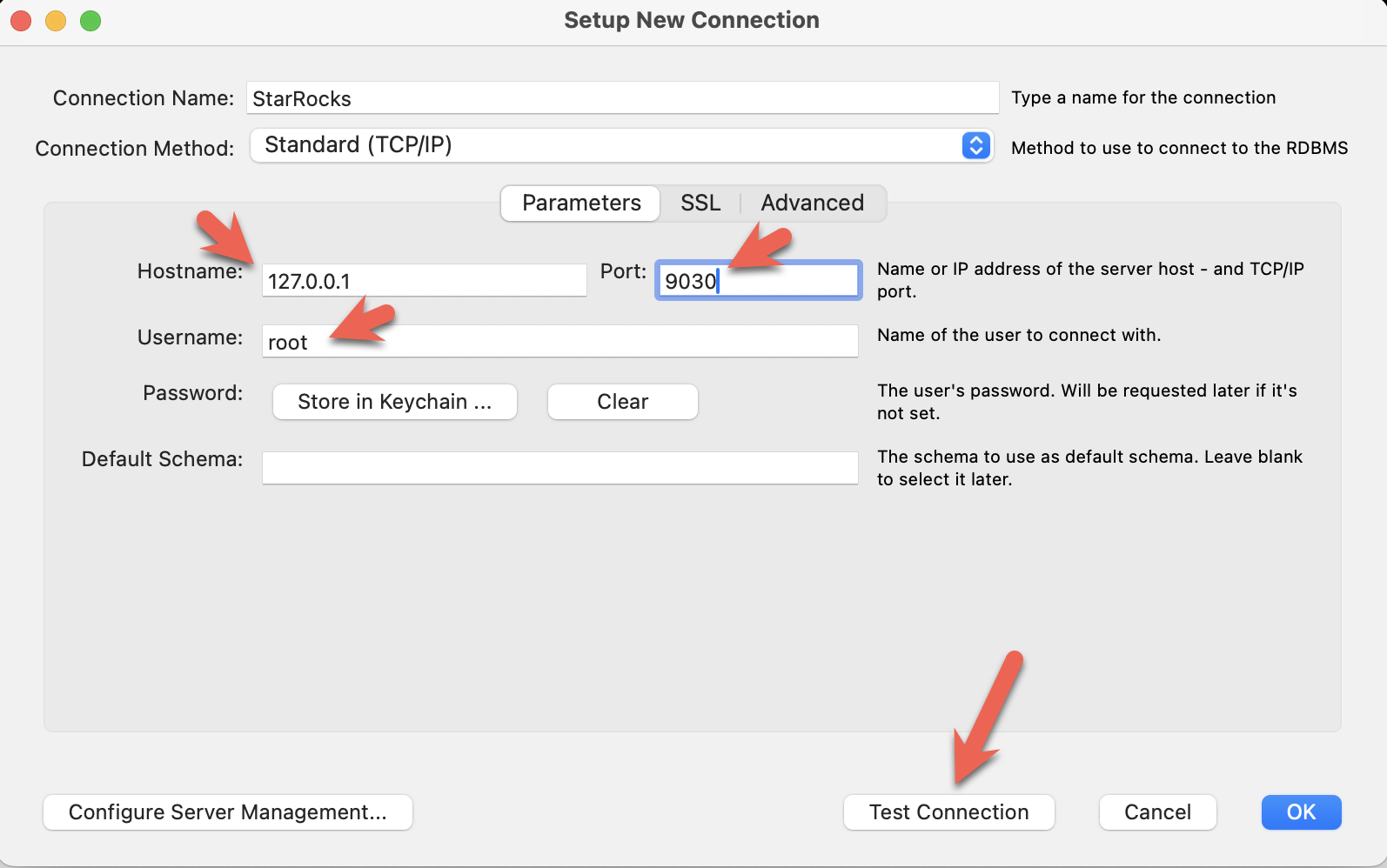
- Install the MySQL Workbench, and add a connection.
- Configure the port, IP, and username and then test the connection:
- You will see warnings from the Workbench as it is checking for a specific MySQL version. You can ignore the warnings and when prompted, you can configure Workbench to stop displaying the warnings:
StarRocks configuration for shared-data
At this point you have StarRocks running, and you have MinIO running. The MinIO access key is used to connect StarRocks and Minio.
This is the part of the FE configuration that specifies that the StarRocks deployment will use shared data. This was added to the file fe.conf when Docker Compose created the deployment.
# enable the shared data run mode
run_mode = shared_data
cloud_native_storage_type = S3
You can verify these settings by running this command from the quickstart directory and looking at the end of the file:
docker compose exec starrocks-fe \
cat /opt/starrocks/fe/conf/fe.conf
:::
Connect to StarRocks with a SQL client
Run this command from the directory containing the docker-compose.yml file.
If you are using a client other than the mysql CLI, open that now.
docker compose exec starrocks-fe \
mysql -P9030 -h127.0.0.1 -uroot --prompt="StarRocks > "
Examine the storage volumes
SHOW STORAGE VOLUMES;
There should be no storage volumes, you will create one next.
Empty set (0.04 sec)
Create a shared-data storage volume
Earlier you created a bucket in MinIO named my-starrocks-volume, and you verified that MinIO has an access key named AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA. The following SQL will create a storage volume in the MionIO bucket using the access key and secret.
CREATE STORAGE VOLUME s3_volume
TYPE = S3
LOCATIONS = ("s3://my-starrocks-bucket/")
PROPERTIES
(
"enabled" = "true",
"aws.s3.endpoint" = "minio:9000",
"aws.s3.access_key" = "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA",
"aws.s3.secret_key" = "BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "false",
"aws.s3.use_aws_sdk_default_behavior" = "false"
);
Now you should see a storage volume listed, earlier it was an empty set:
SHOW STORAGE VOLUMES;
+----------------+
| Storage Volume |
+----------------+
| s3_volume |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
View the details of the storage volume and note that this is nott yet the default volume, and that it is configured to use your bucket:
DESC STORAGE VOLUME s3_volume\G
Some of the SQL in this document, and many other documents in the StarRocks documentation, and with \G instead
of a semicolon. The \G causes the mysql CLI to render the query results vertically.
Many SQL clients do not interpret vertical formatting output, so you should replace \G with ;.
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Name: s3_volume
Type: S3
IsDefault: false
Location: s3://my-starrocks-bucket/
Params: {"aws.s3.access_key":"******","aws.s3.secret_key":"******","aws.s3.endpoint":"minio:9000","aws.s3.region":"us-east-1","aws.s3.use_instance_profile":"false","aws.s3.use_web_identity_token_file":"false","aws.s3.use_aws_sdk_default_behavior":"false"}
Enabled: true
Comment:
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Set the default storage volume
SET s3_volume AS DEFAULT STORAGE VOLUME;
DESC STORAGE VOLUME s3_volume\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Name: s3_volume
Type: S3
IsDefault: true
Location: s3://my-starrocks-bucket/
Params: {"aws.s3.access_key":"******","aws.s3.secret_key":"******","aws.s3.endpoint":"minio:9000","aws.s3.region":"us-east-1","aws.s3.use_instance_profile":"false","aws.s3.use_web_identity_token_file":"false","aws.s3.use_aws_sdk_default_behavior":"false"}
Enabled: true
Comment:
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Create a table
These SQL commands are run in your SQL client.
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS quickstart;
Verify that the database quickstart is using the storage volume s3_volume:
SHOW CREATE DATABASE quickstart \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Database: quickstart
Create Database: CREATE DATABASE `quickstart`
PROPERTIES ("storage_volume" = "s3_volume")
USE quickstart;
CREATE TABLE site_clicks (
`uid` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT "uid",
`site` string NOT NULL COMMENT "site url",
`vtime` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT "vtime"
)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(`uid`)
PROPERTIES("replication_num"="1");
Open the Redpanda Console
There will be no topics yet, a topic will be created in the next step.
http://localhost:8080/overview
Publish data to a Redpanda topic
From a command shell in the routineload/ folder run this command to generate data:
python gen.py 5
On your system, you might need to use python3 in place of python in the command.
If you are missing kafka-python try:
pip install kafka-python
or
pip3 install kafka-python
b'{ "uid": 6926, "site": "https://docs.starrocks.io/", "vtime": 1718034793 } '
b'{ "uid": 3303, "site": "https://www.starrocks.io/product/community", "vtime": 1718034793 } '
b'{ "uid": 227, "site": "https://docs.starrocks.io/", "vtime": 1718034243 } '
b'{ "uid": 7273, "site": "https://docs.starrocks.io/", "vtime": 1718034794 } '
b'{ "uid": 4666, "site": "https://www.starrocks.io/", "vtime": 1718034794 } '
Verify in the Redpanda Console
Navigate to http://localhost:8080/topics in the Redpanda Console, and you will see one topic named test2. Select that topic and then the Messages tab and you will see five messages matching the output of gen.py.
Consume the messages
In StarRocks you will create a Routine Load job to:
- Consume the messages from the Redpanda topic
test2 - Load those messages into the table
site_clicks
StarRocks is configured to use MinIO for storage, so the data inserted into the site_clicks table will be stored in MinIO.
Create a Routine Load job
Run this command in the SQL client to create the Routine Load job, the command will be explained in detail at the end of the lab.
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD quickstart.clicks ON site_clicks
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "JSON",
"jsonpaths" ="[\"$.uid\",\"$.site\",\"$.vtime\"]"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "redpanda:29092",
"kafka_topic" = "test2",
"kafka_partitions" = "0",
"kafka_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
);
Verify the Routine Load job
SHOW ROUTINE LOAD\G
Verify the three highlighted lines:
- The state should be
RUNNING - The topic should be
test2and the broker should beredpanda:2092 - The statistics should show either 0 or 5 loaded rows depending on how soon you ran the
SHOW ROUTINE LOADcommand. If there are 0 loaded rows run it again.
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Id: 10078
Name: clicks
CreateTime: 2024-06-12 15:51:12
PauseTime: NULL
EndTime: NULL
DbName: quickstart
TableName: site_clicks
State: RUNNING
DataSourceType: KAFKA
CurrentTaskNum: 1
JobProperties: {"partitions":"*","partial_update":"false","columnToColumnExpr":"*","maxBatchIntervalS":"10","partial_update_mode":"null","whereExpr":"*","dataFormat":"json","timezone":"Etc/UTC","format":"json","log_rejected_record_num":"0","taskTimeoutSecond":"60","json_root":"","maxFilterRatio":"1.0","strict_mode":"false","jsonpaths":"[\"$.uid\",\"$.site\",\"$.vtime\"]","taskConsumeSecond":"15","desireTaskConcurrentNum":"5","maxErrorNum":"0","strip_outer_array":"false","currentTaskConcurrentNum":"1","maxBatchRows":"200000"}
DataSourceProperties: {"topic":"test2","currentKafkaPartitions":"0","brokerList":"redpanda:29092"}
CustomProperties: {"group.id":"clicks_ea38a713-5a0f-4abe-9b11-ff4a241ccbbd"}
Statistic: {"receivedBytes":0,"errorRows":0,"committedTaskNum":0,"loadedRows":0,"loadRowsRate":0,"abortedTaskNum":0,"totalRows":0,"unselectedRows":0,"receivedBytesRate":0,"taskExecuteTimeMs":1}
Progress: {"0":"OFFSET_ZERO"}
TimestampProgress: {}
ReasonOfStateChanged:
ErrorLogUrls:
TrackingSQL:
OtherMsg:
LatestSourcePosition: {}
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
SHOW ROUTINE LOAD\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Id: 10076
Name: clicks
CreateTime: 2024-06-12 18:40:53
PauseTime: NULL
EndTime: NULL
DbName: quickstart
TableName: site_clicks
State: RUNNING
DataSourceType: KAFKA
CurrentTaskNum: 1
JobProperties: {"partitions":"*","partial_update":"false","columnToColumnExpr":"*","maxBatchIntervalS":"10","partial_update_mode":"null","whereExpr":"*","dataFormat":"json","timezone":"Etc/UTC","format":"json","log_rejected_record_num":"0","taskTimeoutSecond":"60","json_root":"","maxFilterRatio":"1.0","strict_mode":"false","jsonpaths":"[\"$.uid\",\"$.site\",\"$.vtime\"]","taskConsumeSecond":"15","desireTaskConcurrentNum":"5","maxErrorNum":"0","strip_outer_array":"false","currentTaskConcurrentNum":"1","maxBatchRows":"200000"}
DataSourceProperties: {"topic":"test2","currentKafkaPartitions":"0","brokerList":"redpanda:29092"}
CustomProperties: {"group.id":"clicks_a9426fee-45bb-403a-a1a3-b3bc6c7aa685"}
Statistic: {"receivedBytes":372,"errorRows":0,"committedTaskNum":1,"loadedRows":5,"loadRowsRate":0,"abortedTaskNum":0,"totalRows":5,"unselectedRows":0,"receivedBytesRate":0,"taskExecuteTimeMs":519}
Progress: {"0":"4"}
TimestampProgress: {"0":"1718217035111"}
ReasonOfStateChanged:
ErrorLogUrls:
TrackingSQL:
OtherMsg:
LatestSourcePosition: {"0":"5"}
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Verify that data is stored in MinIO
Open MinIO http://localhost:9001/browser/ and verify that there are objects stored under my-starrocks-bucket.
Query the data from StarRocks
USE quickstart;
SELECT * FROM site_clicks;
+------+--------------------------------------------+------------+
| uid | site | vtime |
+------+--------------------------------------------+------------+
| 4607 | https://www.starrocks.io/blog | 1718031441 |
| 1575 | https://www.starrocks.io/ | 1718031523 |
| 2398 | https://docs.starrocks.io/ | 1718033630 |
| 3741 | https://www.starrocks.io/product/community | 1718030845 |
| 4792 | https://www.starrocks.io/ | 1718033413 |
+------+--------------------------------------------+------------+
5 rows in set (0.07 sec)
Publish additional data
Running gen.py again will publish another five records to Redpanda.
python gen.py 5
Verify that data is added
Since the Routine Load job runs on a schedule (every 10 seconds by default), the data will be loaded within a few seconds.
SELECT * FROM site_clicks;
+------+--------------------------------------------+------------+
| uid | site | vtime |
+------+--------------------------------------------+------------+
| 6648 | https://www.starrocks.io/blog | 1718205970 |
| 7914 | https://www.starrocks.io/ | 1718206760 |
| 9854 | https://www.starrocks.io/blog | 1718205676 |
| 1186 | https://www.starrocks.io/ | 1718209083 |
| 3305 | https://docs.starrocks.io/ | 1718209083 |
| 2288 | https://www.starrocks.io/blog | 1718206759 |
| 7879 | https://www.starrocks.io/product/community | 1718204280 |
| 2666 | https://www.starrocks.io/ | 1718208842 |
| 5801 | https://www.starrocks.io/ | 1718208783 |
| 8409 | https://www.starrocks.io/ | 1718206889 |
+------+--------------------------------------------+------------+
10 rows in set (0.02 sec)
Configuration details
Now that you have experienced using StarRocks with shared-data it is important to understand the configuration.
CN configuration
The CN configuration used here is the default, as the CN is designed for shared-data use. The default configuration is shown below. You do not need to make any changes.
sys_log_level = INFO
# ports for admin, web, heartbeat service
be_port = 9060
be_http_port = 8040
heartbeat_service_port = 9050
brpc_port = 8060
starlet_port = 9070
FE configuration
The FE configuration is slightly different from the default as the FE must be configured to expect that data is stored in Object Storage rather than on local disks on BE nodes.
The docker-compose.yml file generates the FE configuration in the command.
# enable shared data, set storage type, set endpoint
run_mode = shared_data
cloud_native_storage_type = S3
This config file does not contain the default entries for an FE, only the shared-data configuration is shown.
The non-default FE configuration settings:
Many configuration parameters are prefixed with s3_. This prefix is used for all Amazon S3 compatible storage types (for example: S3, GCS, and MinIO). When using Azure Blob Storage the prefix is azure_.
run_mode=shared_data
This enables shared-data use.
cloud_native_storage_type=S3
This specifies whether S3 compatible storage or Azure Blob Storage is used. For MinIO this is always S3.
Details of CREATE storage volume
CREATE STORAGE VOLUME s3_volume
TYPE = S3
LOCATIONS = ("s3://my-starrocks-bucket/")
PROPERTIES
(
"enabled" = "true",
"aws.s3.endpoint" = "minio:9000",
"aws.s3.access_key" = "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA",
"aws.s3.secret_key" = "BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "false",
"aws.s3.use_aws_sdk_default_behavior" = "false"
);
aws_s3_endpoint=minio:9000
The MinIO endpoint, including port number.
aws_s3_path=starrocks
The bucket name.
aws_s3_access_key=AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
The MinIO access key.
aws_s3_secret_key=BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
The MinIO access key secret.
aws_s3_use_instance_profile=false
When using MinIO an access key is used, and so instance profiles are not used with MinIO.
aws_s3_use_aws_sdk_default_behavior=false
When using MinIO this parameter is always set to false.
Notes on the Routine Load command
StarRocks Routine Load takes many arguments. Only the ones used in this tutorial are described here, the rest will be linked to in the more information section.
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD quickstart.clicks ON site_clicks
PROPERTIES
(
"format" = "JSON",
"jsonpaths" ="[\"$.uid\",\"$.site\",\"$.vtime\"]"
)
FROM KAFKA
(
"kafka_broker_list" = "redpanda:29092",
"kafka_topic" = "test2",
"kafka_partitions" = "0",
"kafka_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
);
Parameters
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD quickstart.clicks ON site_clicks
The parameters for CREATE ROUTINE LOAD ON are:
- database_name.job_name
- table_name
database_name is optional. In this lab, it is quickstart and is specified.
job_name is required, and is clicks
table_name is required, and is site_clicks
Job properties
Property format
"format" = "JSON",
In this case, the data is in JSON format, so the property is set to JSON. The other valid formats are: CSV, JSON, and Avro. CSV is the default.
Property jsonpaths
"jsonpaths" ="[\"$.uid\",\"$.site\",\"$.vtime\"]"
The names of the fields that you want to load from JSON-formatted data. The value of this parameter is a valid JsonPath expression. More information is available at the end of this page.
Data source properties
kafka_broker_list
"kafka_broker_list" = "redpanda:29092",
Kafka's broker connection information. The format is <kafka_broker_name_or_ip>:<broker_ port>. Multiple brokers are separated by commas.
kafka_topic
"kafka_topic" = "test2",
The Kafka topic to consume from.
kafka_partitions and kafka_offsets
"kafka_partitions" = "0",
"kafka_offsets" = "OFFSET_BEGINNING"
These properties are presented together as there is one kafka_offset required for each kafka_partitions entry.
kafka_partitions is a list of one or more partitions to consume. If this property is not set, then all partitions are consumed.
kafka_offsets is a list of offsets, one for each partition listed in kafka_partitions. In this case the value is OFFSET_BEGINNING which causes all of the data to be consumed. The default is to only consume new data.
Summary
In this tutorial you:
- Deployed StarRocks, Reedpanda, and Minio in Docker
- Created a Routine Load job to consume data from a Kafka topic
- Learned how to configure a StarRocks Storage Volume that uses MinIO
More information
The sample used for this lab is very simple. Routine Load has many more options and capabilities. learn more.
